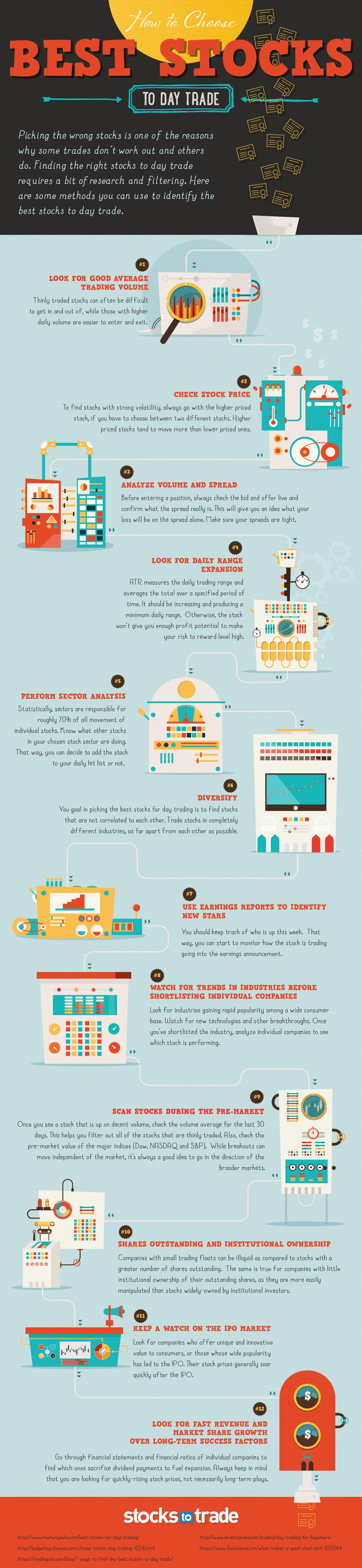
Offshore financial services refer to activities that are conducted by companies outside their jurisdiction's regulatory borders. These services may include fund administration, insurance, trust, tax planning, IBC, and fund management. These activities are typically performed in offshore financial centres, which are generally tax-free. However, most offshore financial centers do not have to be regulated by law.
Tax-free offshore financial services
Many offshore financial services can be tax-free and beneficial to individuals or companies. Trusts are an excellent example. Trusts are able to manage large sums of money without any taxation. You can find offshore banking services in many jurisdictions including Anguilla, Bermuda, and Cayman Islands.
The offshore industry has advanced and matured significantly in recent times. Many of its components are similar to those that existed a century ago. The international system of state, which recognizes the sovereign as being the highest legal authority, gave rise to the offshore world.
OFCs have a specialization in offshore financial service.
Offshore financial services are those transactions performed outside of the jurisdictions of the main onshore economies. These services are provided via offshore financial centers which are spread around the globe. Many of these jurisdictions can be found in small, independent islands or semi-independent ones located in Western Europe or the Caribbean. They can also exist in Asia.
OFCs have a geographic focus and are often specialized in certain activities. The Netherlands acts as an intermediary between European companies, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. The United Kingdom is another example, and it is an offshore hub for companies from the United Kingdom as well as former British Empire members.
The regulation of offshore financial services is not the same in every jurisdiction.
Companies offering offshore financial services are exempt from the laws of their home countries. These companies are usually multinationals. Many of these companies have complex corporate structures. For example, HSBC is made up of 828 legal corporate entities spread across 71 different jurisdictions. This structure is used to reduce costs and accountability. Many of these companies have offshore financial centers such as Bermuda and British Virgin Islands.
Offshore financial services have not been completely regulated, even though the industry has become highly politicized. The majority of corporate use OFCs occurs in a few key jurisdictions, many of which are OECD.

Offshore financial Services are a third type
Offshore financial services are often exempt from scrutiny by foreign governments. Luxembourg was a popular destination for foreign investors during the 1970s. It had a low income tax, no withholding taxes on dividend income earned by non-residents, and banking secrets laws. Similar opportunities were provided by the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Bahrain was an oil surplus collection center in the Middle East. It passed banking laws and tax incentives which made offshore banking possible. Other examples of offshore banking include the Cayman Islands and the Netherlands.
There are many offshore financial centers that specialize in certain activities. They are less regulated and offer fewer specialist services. They are attractive to large financial institutions due to their tax benefits.
FAQ
Is it really worth investing in gold?
Since ancient times, gold has been around. It has remained valuable throughout history.
But like anything else, gold prices fluctuate over time. When the price goes up, you will see a profit. If the price drops, you will see a loss.
No matter whether you decide to buy gold or not, timing is everything.
What are the types of investments available?
Today, there are many kinds of investments.
These are some of the most well-known:
-
Stocks: Shares of a publicly traded company on a stock-exchange.
-
Bonds are a loan between two parties secured against future earnings.
-
Real Estate - Property not owned by the owner.
-
Options – Contracts allow the buyer to choose between buying shares at a fixed rate and purchasing them within a time frame.
-
Commodities – Raw materials like oil, gold and silver.
-
Precious metals – Gold, silver, palladium, and platinum.
-
Foreign currencies - Currencies other that the U.S.dollar
-
Cash - Money which is deposited at banks.
-
Treasury bills - The government issues short-term debt.
-
A business issue of commercial paper or debt.
-
Mortgages – Loans provided by financial institutions to individuals.
-
Mutual Funds - Investment vehicles that pool money from investors and then distribute the money among various securities.
-
ETFs - Exchange-traded funds are similar to mutual funds, except that ETFs do not charge sales commissions.
-
Index funds: An investment fund that tracks a market sector's performance or group of them.
-
Leverage: The borrowing of money to amplify returns.
-
ETFs - These mutual funds trade on exchanges like any other security.
The best thing about these funds is they offer diversification benefits.
Diversification means that you can invest in multiple assets, instead of just one.
This protects you against the loss of one investment.
Can I lose my investment?
You can lose it all. There is no way to be certain of your success. However, there is a way to reduce the risk.
Diversifying your portfolio is a way to reduce risk. Diversification allows you to spread the risk across different assets.
You could also use stop-loss. Stop Losses allow shares to be sold before they drop. This reduces the risk of losing your shares.
You can also use margin trading. Margin Trading allows to borrow funds from a bank or broker in order to purchase more stock that you actually own. This increases your profits.
How can I invest wisely?
It is important to have an investment plan. It is vital to understand your goals and the amount of money you must return on your investments.
It is important to consider both the risks and the timeframe in which you wish to accomplish this.
This will allow you to decide if an investment is right for your needs.
Once you've decided on an investment strategy you need to stick with it.
It is better not to invest anything you cannot afford.
Statistics
- According to the Federal Reserve of St. Louis, only about half of millennials (those born from 1981-1996) are invested in the stock market. (schwab.com)
- As a general rule of thumb, you want to aim to invest a total of 10% to 15% of your income each year for retirement — your employer match counts toward that goal. (nerdwallet.com)
- Some traders typically risk 2-5% of their capital based on any particular trade. (investopedia.com)
- They charge a small fee for portfolio management, generally around 0.25% of your account balance. (nerdwallet.com)
External Links
How To
How to invest and trade commodities
Investing in commodities involves buying physical assets like oil fields, mines, plantations, etc., and then selling them later at higher prices. This is known as commodity trading.
Commodity investment is based on the idea that when there's more demand, the price for a particular asset will rise. The price falls when the demand for a product drops.
You want to buy something when you think the price will rise. You want to sell it when you believe the market will decline.
There are three main categories of commodities investors: speculators, hedgers, and arbitrageurs.
A speculator is someone who buys commodities because he believes that the prices will rise. He doesn't care whether the price falls. A person who owns gold bullion is an example. Or, someone who invests into oil futures contracts.
An investor who buys commodities because he believes they will fall in price is a "hedger." Hedging is a way to protect yourself against unexpected changes in the price of your investment. If you are a shareholder in a company making widgets, and the value of widgets drops, then you might be able to hedge your position by selling (or shorting) some shares. This is where you borrow shares from someone else and then replace them with yours. The hope is that the price will fall enough to compensate. The stock is falling so shorting shares is best.
The third type, or arbitrager, is an investor. Arbitragers trade one thing for another. For example, you could purchase coffee beans directly from farmers. Or you could invest in futures. Futures allow the possibility to sell coffee beans later for a fixed price. You are not obliged to use the coffee bean, but you have the right to choose whether to keep or sell them.
This is because you can purchase things now and not pay more later. If you know that you'll need to buy something in future, it's better not to wait.
However, there are always risks when investing. One risk is that commodities prices could fall unexpectedly. Another risk is that your investment value could decrease over time. These risks can be reduced by diversifying your portfolio so that you have many types of investments.
Another thing to think about is taxes. It is important to calculate the tax that you will have to pay on any profits you make when you sell your investments.
Capital gains taxes should be considered if your investments are held for longer than one year. Capital gains taxes only apply to profits after an investment has been held for over 12 months.
If you don’t intend to hold your investments over the long-term, you might receive ordinary income rather than capital gains. For earnings earned each year, ordinary income taxes will apply.
In the first few year of investing in commodities, you will often lose money. As your portfolio grows, you can still make some money.